What Is Port Forwarding and How Does It Work?
Port forwarding, also known as port mapping, gives external network access to devices within your private network. It makes external connections much easier and ensures that your router won't block necessary connections because they aren't recognized. In this article, we'll break down port forwarding for even the most novice of Internet users.
What is port forwarding?
Port forwarding, also known as port mapping, is an application of network address translation (NAT). It's the method for directing external traffic to the appropriate device inside a local area network to openings, called ports. Sometimes, firewalls register safe Internet traffic as unsafe because it comes from an external source and attempts to connect through potentially vulnerable ports.
It allows you to specify which traffic can enter your local area network (LAN) through designated ports. The process can help run a public HTTP server within a private LAN, permit Secure Shell access to a host on the private LAN from the Internet, run a game server within a private LAN, and more.
How does port forwarding work?
Port forwarding works similarly to the way phones forward calls to the appropriate lines. Say you call your credit card company and want to connect to an administrator to talk about your account. However, it’s an auto-attendant that answers and informs you that you can press 1 to hear your balance, 2 to make a payment, or 3 to talk to an administrator.
You press 3 and to direct your call to the appropriate line, clearing the line for other calls and fulfilling your connection request at the same time.
The auto-attendant does the same job as your router. Your router receives requests from an external IP address with a specified port and sends that request to the mapped internal IP address. The internal listening device on the assigned port can then establish a connection to the external requesting device. Port forwarding maps an external port directly to an internal IP address and open port.
Note that there’s a difference between an Internet IP address and a NAT (local) IP address. All routers have an IP address. But each device in your home under the router has a local IP address, which identifies it uniquely. Routers forward traffic to devices using their NAT IP addresses, rather than the router’s IP address.
Therefore, when using a router or modem, you need port forwarding to get connections to the correct local IP address. The router receives the incoming connection, but it isn't equipped to handle that request without instructions; the router needs to know which machine on your local area network to send the request to. Without a port forward instruction in place, the request will fail.
The router can only port forward this request to one PC at a time; therefore, if you're running more than one machine, you need to change the default port and forward it as necessary.
Understanding the port numbering system
The ports used aren’t physical ports located on your computer or router. They’re virtual ports. They exist as a part of the TCP/IP and UDP protocols. Though there are 65536 ports available in total, connections most often use lower-numbered ports.
For example, take Windows Remote Desktop Connection, also known as Terminal Services. Terminal services, by default, listens on port 3389. Open the Remote Desktop Client and type in an IP address; the client will attempt to connect to that IP on port 3389 because it has been routed to consistently connect to that port.
Many common connections use the same port numbers regardless of device. File Transfer Protocol (FTP) uses port 21. Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) uses port 25 or port 587. See our port scanner for a longer list of common port numbers and their connections.
What is port forwarding used for?
Though port forwarding may seem as if it has little purpose for the average Internet user, there are benefits even for those who aren’t well-versed in technological knowledge. Configuring your router helps communication apps like Skype. Your router may block Skype’s ports, limiting your access to their services. Port forwarding fixes the issue and allows you to keep communicating as normal.
Online gaming is one of the most popular reasons that users choose to port forward. While it’s not necessary for gameplay, port forwarding makes your gaming console or PC more accessible on the game server across the Internet. It improves connections to other consoles. Port forwarding also improves network connection speed, lobby wait times, and overall gameplay, especially for those who host.
Minecraft port forwarding
For Minecraft users, port forwarding is almost a necessity. The game builds upon interactions between users into other users' constructed worlds, which means servers are essential to the game.
If you set up your own Minecraft server, you'll need to port forward on your local network in order to make sure incoming traffic can connect. The default Minecraft port is 25565. Make sure you have access to your local network and follow the instructions below to add a custom service and create the port connection.
If you choose to port forward for any other game, know that configuring your router to port forward for your PlayStation or Xbox is safe; there's no need to worry about harmful traffic coming through the port or across your WiFi.
How to set up port forwarding on a router
Port forwarding on the router is a fairly simple process, though it varies by each router model and manufacturer. Regardless of the router, however, the first step to setting up port forwarding on a router is to access your router’s IP address.
Many routers use similar IP addresses. 192.168.0.1, 192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.254, and 10.0.0.1 are all common router IP addresses.
If you don’t know the IP address of your device, you can find it on the WhatIsMyIP.com router login chart or from your computer.
- For Windows computers, open command prompt and enter ipconfig. You’ll see the default gateway, among other information.
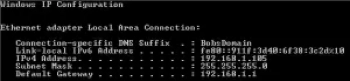
- For Mac computers, use the netstat -nr
- For Linux computers, use the command route.
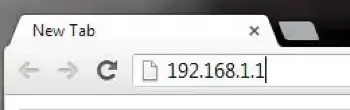
Take note of the default gateway as your router IP. Do the same on the computer you use as a server for your internal IP. Once you have your router’s IP address, enter it into your web browser address bar as seen below.
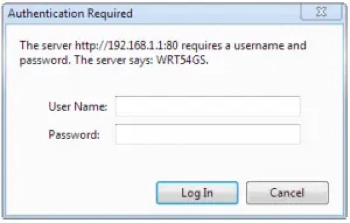
You’ll need the username and password for your router, which can be found on the router login chart on our page or on the bottom or back of your router. Enter the default username and password.
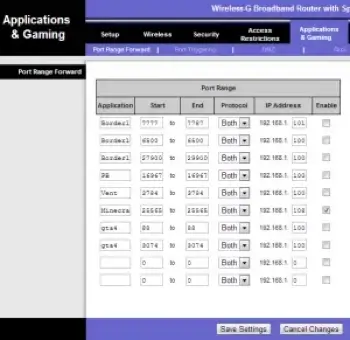
Once you’ve logged in to your router, locate the port forwarding settings. The location of your port forwarding settings depends on the router manufacturer. Most routers have it under the Advanced settings section. For Linksys routers, check the Applications and Gaming tab.
Within the port forwarding settings, you will see either a list (as seen below on the Linksys router) or a section to add new port forwarding rules. Enter the IP of the computer running your server and take note of what port the server uses. Look at the examples below of actual ports needed to forward for certain games and servers in order for the games to function properly. After adding your entries, make sure you enable your forwarding and save your settings.
Your server should now be able to receive incoming connections through your router. However, in order to successfully and completely set up port forwarding on a router, you need to ensure the proper ports are open not only on your router but also on any other screening software downloaded to your operating system, like a firewall or antivirus program.
If you follow these steps to port forward on your router and find that the port checker still shows your ports as closed, you may need to go through those programs and configure them to also allow traffic through to the selected ports.
Port forwarding risks
Port forwarding has many benefits for Internet users, but like anything, it isn’t entirely risk-free.
A common fear users have is whether port forwarding is safe because it inherently gives people and users outside of your network more remote access to your computer. This poses a risk; hackers have a better chance of getting to your device if you access or give access to unsafe ports.
Furthermore, it also requires disabling network access translation (NAT). It gives your devices separate IP addresses, which is necessary for port forwarding, but it also disables a system which protects your device from external attacks.
It's also worth considering that the actions you take when port forwarding could have an affect on your safety. If you connect to game servers and accidentally contract a virus, that damages your device. If hacked, you could lose personal information like your usernames and passwords, bank account information, or anything linked to the damaged device.
However, if you take the proper precautions, port forwarding is a safe and secure process. As a rule, only connect to stable and secure ports. Remember to use strong, secure passwords and update your device's security and operating system regularly.
Browse on private networks if possible and make sure your security firewall is installed and active. Many devices have firewalls automatically installed; if that's the case, you can port forward without concerns.
What is DMZ on a router?
When understanding how to port forward, it’s equally as important to understand DMZ networks. On a router, DMZs – which stands for demilitiarized zones – are subnets that separate local area networks from other untrusted networks. Any services that a computer user accesses on the public Internet – the web, email, DNS, or other servers – should be placed in the DMZ network in order to protect the rest of the local network.
Using a DMZ on a router offers protection and control to users on a router. They isolate potential dangers, reduce the control external users have on internal systems, and help make necessary resources safely available to other external users. However, it also increases the risks mentioned above.
A DMZ allows you to open all ports and forward all incoming traffic to a device. This strips the device in the DMZ of its firewall protection. Essentially, it becomes incredibly vulnerable and can be attacked by anyone scanning for IP addresses with open ports.
Generally, do not enable DMZ on your router for prolonged periods of time. The loss of router protection via hardware firewall puts your security at risk. If you are having trouble port forwarding, you can temporarily put a device in the DMZ for troubleshooting purposes only.
If the device does not work unless in the DMZ, install a software firewall on that device. Then, for security purposes, block all ports that way except the port you are attempting to open.
Frequently asked questions
Do I need port forwarding?
No, you don't need port forwarding for most day-to-day functions as an Internet user. However, many users will find it helpful in order to speed upload and download times for their device. Furthermore, if you encounter an issue where your router blocks a certain port, like with Skype, you may need to forward in order to get it operational again.
Is port forwarding safe?
Port forwarding is safe to do as long as you take the proper precautions. Protect your computer with a firewall and only connect to secure ports in order to make port forwarding a safe process.
What is SSH port forwarding?
SSH stands for secure shell or secure socket shell. SSH port forwarding tunnels application ports from the client machine to the server machine, which is useful for going through firewalls or opening backdoors into internal networks. Hackers can abuse it, but it isn't innately malicious. You can do SSH port forwarding remotely; once a connection is made to a port, the connection is forwarded over the existing SSH channel to the server's port.
What’s the difference between port forwarding and port triggering?
Port triggering is a dynamic type of port forwarding, so they aren't entirely separate. However, the difference is that port forwarding is used when the user needs to reach multiple local computers at once. It also works when applications need to open incoming ports that are different than the outgoing ports. It doesn't open ports and keep them open, like traditional port forwarding; rather, the ports remain closed when not actively in use and only open when they're needed.
What is port mapping?
Port mapping is another term for port forwarding. It's a way to direct external traffic to the correct device inside a local area network, or LAN.